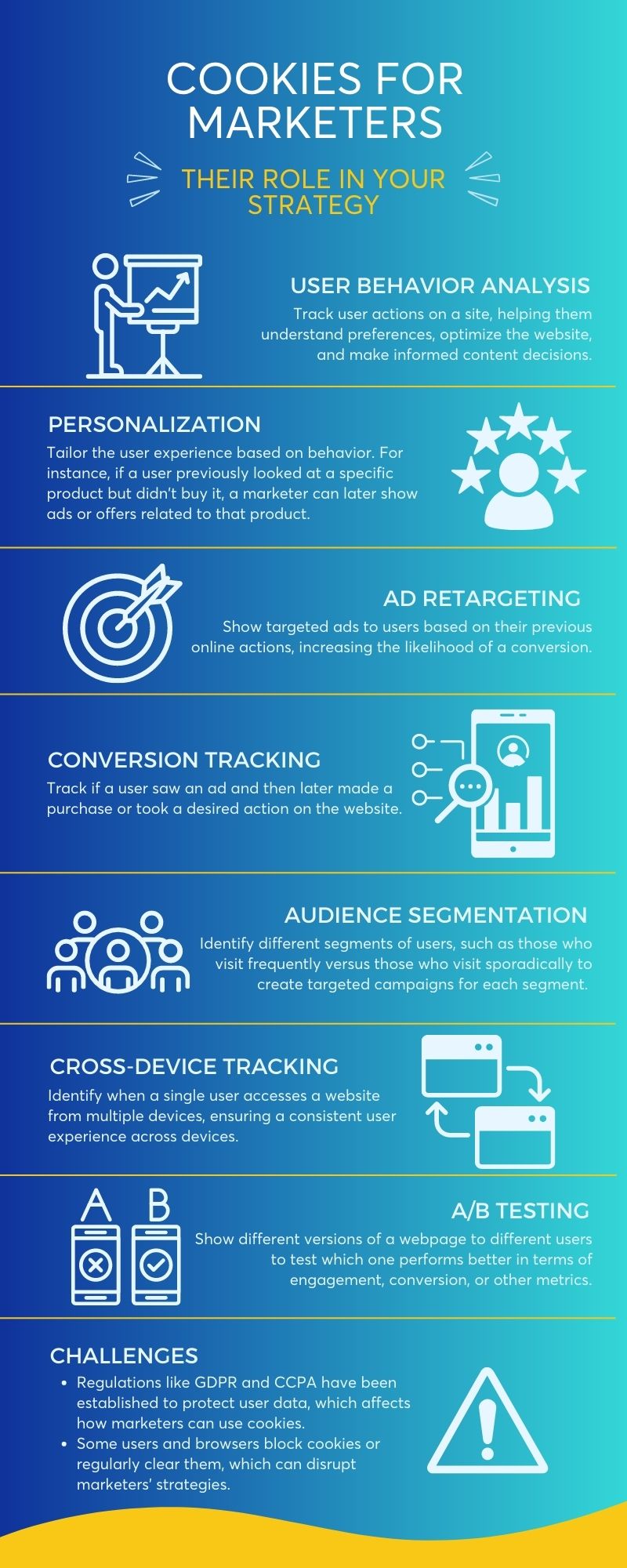
In the vast digital realm, cookies are central to the way websites function and how user experiences are tailored. This article demystifies the first-party cookie and third-party cookie, highlighting their differences and purposes. Dive in to understand how they shape your online interactions and why they’re pivotal in today’s web ecosystem.
What are Cookies?
Cookies are created by domains that a user visits and serve various functions. From remembering login details to collecting analytics data, cookies allow website owners to enhance user experience and gain insights. The two most prominent types are the first-party and third-party cookies.
How are First-Party Cookies Created?
When you visit a website, a first-party cookie is set by that particular domain. These cookies are primarily used to remember user settings, manage sessions, and enhance user experience. Web browsers automatically accept first-party cookies as they’re generally considered non-intrusive and beneficial for users. For instance, a website that remembers your preferred language or login details uses first-party cookies.
Why Use Third-Party Cookies?
Third-party cookies are created by domains different from the one you’re visiting. These cookies allow third-party service providers, especially advertisers, to track users across different websites, facilitating cross-site tracking and targeted advertising. They are also vital for website owners to collect analytics data and understand user behavior across multiple sites.
First Party vs. Third Party: Where Do These Cookies Originate?
While a first-party cookie is set by the website you’re visiting, a third-party cookie can be set by a third-party server, often from a different website. For instance, when you visit a website that loads an advertisement from a third-party server, it’s this third-party server that creates the third-party cookie.
How do Cookies Track User Activity?
Cookies track user behavior by storing specific data snippets. First-party cookies generally remember user preferences, while third-party cookies track users across various websites, gathering data for targeted advertising and analytics.
Are All Cookies Created Equal?
Definitely not! There are many types of cookies, including second-party cookies, which are cookies shared between two parties in agreement, though these are less common. Then there’s the difference between first-party and third-party cookies in terms of origin, purpose, and perception. While first-party cookies are seen as benign and user-centric, third-party cookies often receive flak for potential privacy concerns.
Can We Manage Cookies?
Absolutely! Most browsers allow users to manage cookies, choose which ones to accept, block third-party cookies, and even clear all stored cookies. As privacy concerns rise, many users are opting to block third-party cookies by default.
Why are Some Browsers Blocking Third-Party Cookies?
Given rising privacy concerns, some browsers, like Chrome, will start blocking third-party cookies. The primary reasons are to limit cross-site tracking and to give users more control over their data. With third-party cookies in the crosshairs, it’s worth noting that not all third-party data is eliminated; some data collection is still permissible.
Purpose of First-Party Cookies: Beyond Basic Functionality?
While the basic functionality of first-party cookies lies in enhancing user experience, they also play a role in analytics. These cookies allow website owners to collect specific data about user behavior on their site, offering insights into performance and areas for improvement.
The Future: Life Without Third-Party Cookies?
With browsers phasing out third-party cookies and a global shift towards privacy, marketers and website owners need to adapt. Relying more on first-party data and exploring alternatives like fingerprinting may become the norm. Still, the focus will always remain on balancing user experience with privacy concerns.
Key Takeaways:
- Cookies are central to web functionality, with first-party cookies being set by the visited website and third-party cookies by other domains.
- First-party cookies are generally used for enhancing user experience, while third-party cookies are used mainly for advertising and analytics.
- Users can manage and even block cookies, especially third-party ones, for privacy reasons.
- The future may see a decline in the use of third-party cookies, pushing businesses to find alternatives.
With this knowledge in hand, you’re better equipped to navigate the digital landscape, understanding the role cookies play in your online journey.
Ready to elevate your tracking game? Reach out to Wizaly today – where all your tracking needs are not just met, but surpassed.



